Asia
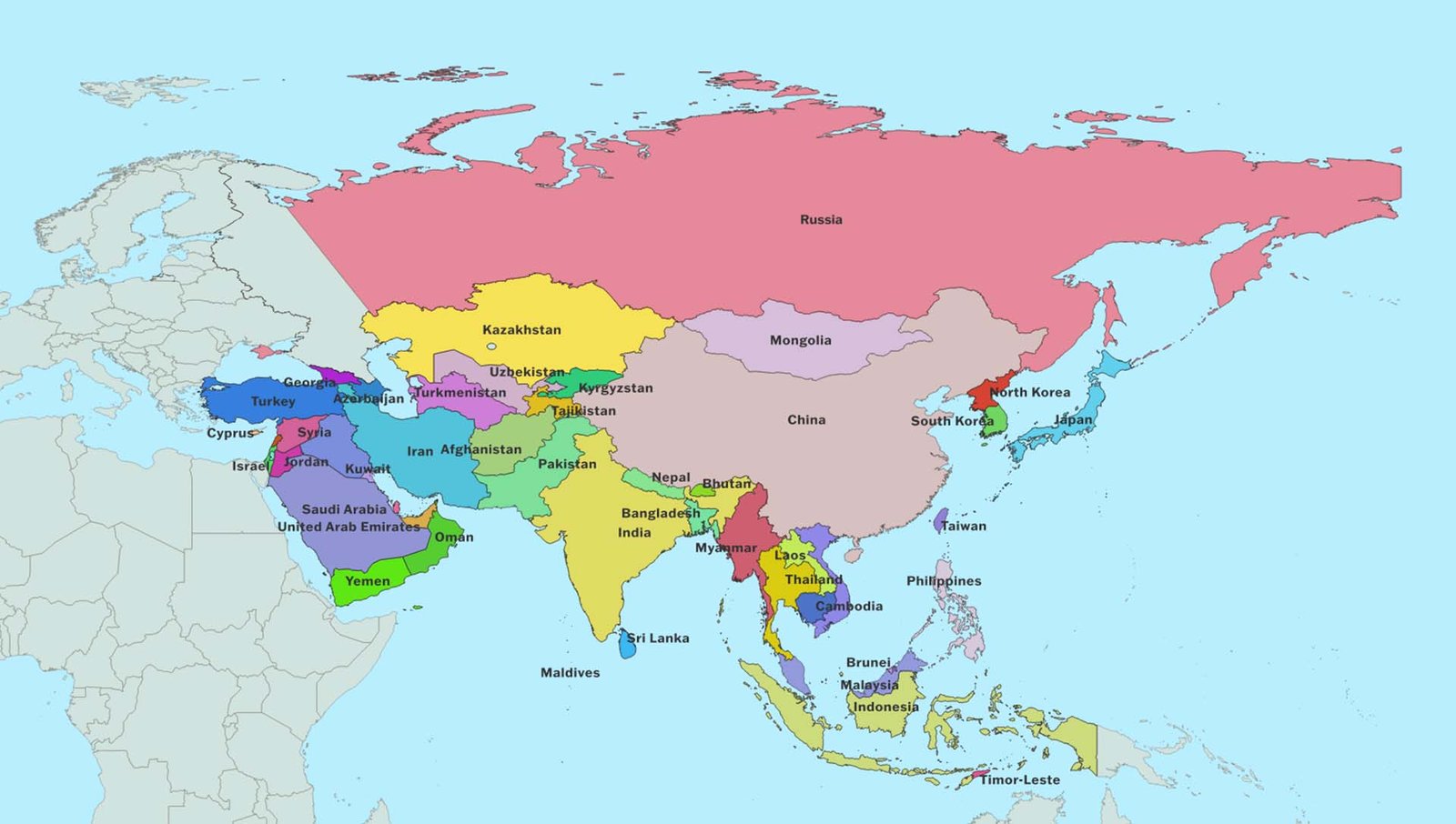
Asia is the largest continent in the world. Asia covers 29.8% of the land, and it has 60% of the world’s population. The continent is made up of 48 countries and three other territories.
Location: Asia is located in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres. It forms the eastern part of the larger Eurasian landmass. Asia is surrounded by several bodies of water. To the north is the Arctic Ocean. The Pacific Ocean lies to the east. The Indian Ocean is to the south. The western border is less clear, featuring the Ural Mountains and the Black Sea.
History of Asia
How did Asia get its name?
The name “Asia” originated from the Greek word ‘Ἀσία’ (Asia). At first, this referred to Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) and the lands east of Greece and the Aegean Sea. The word Asia likely comes from the Bronze Age Hittite name “Assuwa”, a region in northwestern Anatolia. Over time, the term’s meaning spread eastward, and the Romans used it for one of their provinces. Later, it came to mean the whole continent.
Ancient to Classical Eras
~60,000 BCE, early human habitation in India was recorded.
About 3300–1300 BCE, the Indus Valley Civilization thrived. This was a key Bronze Age culture in the western Indian subcontinent.
~1600–1100 BCE, the Shang Dynasty appeared in China. It used oracle bones and excelled in bronze casting.
~1100–221 BCE, the Zhou Dynasty came next. During this time, cast iron was developed. Philosophies like Confucianism and Taoism also emerged.
c. 802 CE, the founders established the Khmer Empire in Southeast Asia.
c. 1000 CE, the Chola Empire dominated parts of South and Southeast Asia.
Medieval to Early Modern periods
~1000–1700s CE: The Chola Empire, along with the Srivijayan and Khmer Empires, thrived and shaped the region.
c. 1600–1900 CE: European colonial powers set up colonies in Asia. The Dutch took control of Indonesia, while the British influenced India.
19th century: British power expands in places like India. The Opium Wars also affect China.
Modern Era
Early 20th century: Japanese expansionism rises as a major force. This causes conflict with China during the Second Sino-Japanese War. In 1947, the partition of India results in the formation of India and Pakistan.
1949: The People’s Republic of China is established.
1991: The Soviet Union collapsed, leading to a major change. Former Asian republics became independent.
Late 20th Century: China and India made significant economic reforms. They opened their economies to the world.
Geography of Asia
Regions:
It is geographically divided into regions:
-
Northern Asia: Russia, Kazakhstan, Mongolia.
-
Western Asia (Middle East): Turkey, Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Iran, Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Oman, Yemen
-
Central Asia: Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan (partly in Northern Asia, too).
-
Southern Asia: India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, the Maldives, and Afghanistan.
-
Eastern Asia: China, Japan, North Korea, South Korea, Taiwan
Southeast Asia: Myanmar (Burma), Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Brunei, the Philippines, and Timor-Leste.
Asia is the birthplace of all the world’s major religions—Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, and Judaism