The Vice President of a country holds the second-highest office, ranking directly below the President in terms of precedence. The role is often designed to serve as a key constitutional position, providing support to the President and assuming the presidency in case of vacancy. In many countries, including India, the office is modelled on the lines of the American Vice President, reflecting similarities in responsibilities and constitutional functions.
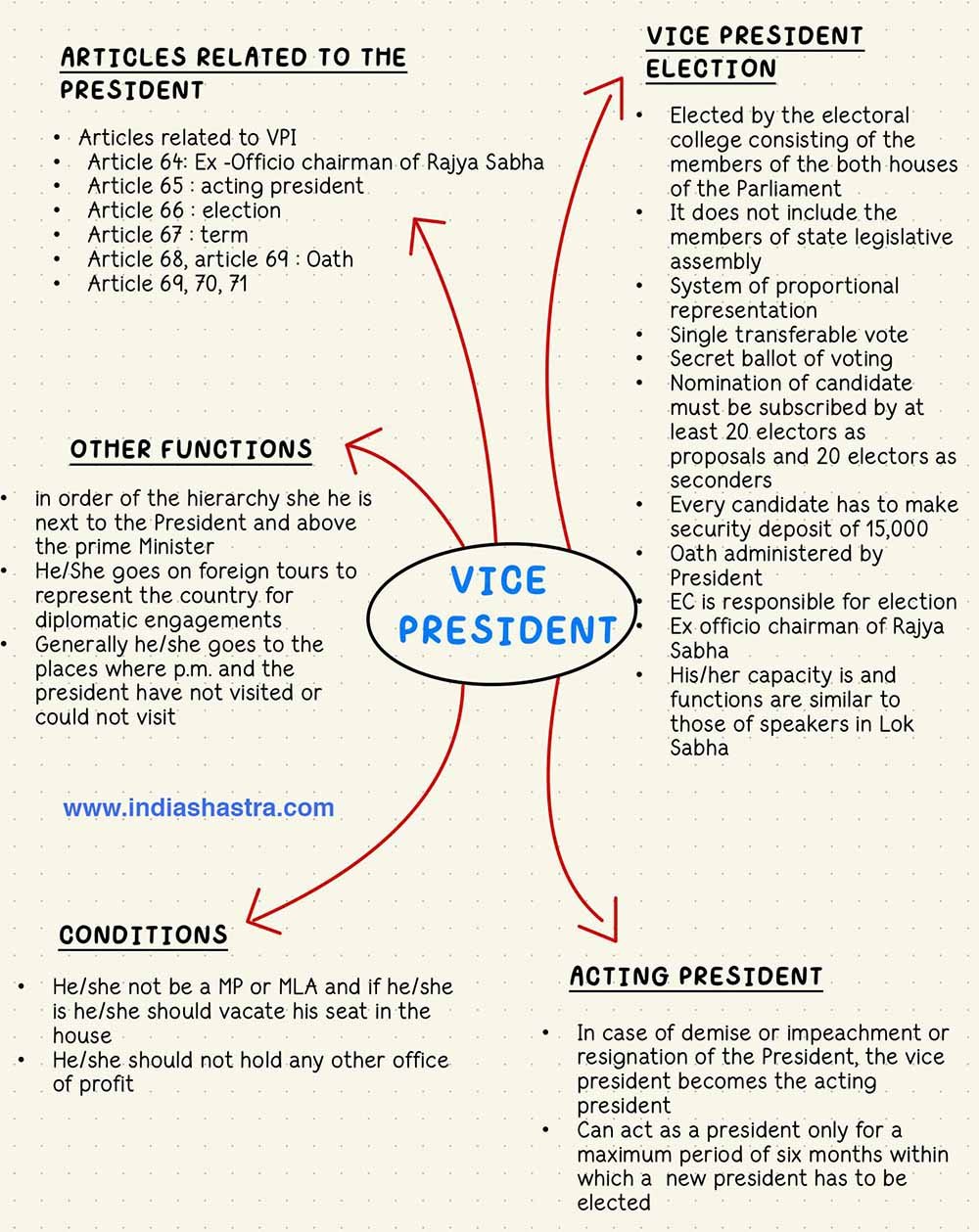
Articles 63 to 71 describe the constitutional responsibilities, duties and positional rights of the vice president of India. As per Article 63 of the Indian Constitution, it is stated that there shall be a Vice President of India.
Election to the Office of Vice President
But how is the Vice President selected to his/ her office? What are the procedures involved? These are all dictated in Article 65 of the Indian Constitution, which mentions the qualifications for the candidate as well as the election procedure for the same. The following is the way in which Article 66 mandates the election process of the Vice President of India:
- The Vice-President is elected by an electoral college, consisting of the members of both Houses of Parliament, using a system of proportional representation by means of a single transferable vote.
- The election is conducted by secret ballot.
It also notes the following qualifications a candidate must meet:
- Shall be a citizen of India.
- Must be at least 35 years of age.
- Should be qualified to be elected as a member of the Rajya Sabha.
- They must not hold any office of profit under the Government of India, state governments, or local authorities.
- However, a sitting President, Vice-President, governor of any state, or a minister at the Union or state level is not considered to hold an office of profit and is eligible to contest for the Vice-President’s office.
- A candidate must have their nomination supported by 20 proposers and 20 seconders and deposit ₹15,000 as security in the Reserve Bank of India.
The Vice-President of India is elected through an indirect election by an electoral college comprising both elected and nominated members of Parliament, unlike the President, whose electoral college includes only elected members of Parliament and state legislative assemblies. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar explained this distinction by noting that, while the President’s powers extend to both the Centre and states, the Vice-President’s primary role is to preside over the Rajya Sabha, with limited involvement in state matters.
Additionally, the election cannot be invalidated due to vacancies in the electoral college, and actions performed by a Vice-President remain valid before the declaration that the election is declared void by the Supreme Court.
Oath to the office of Vice President
As per Article 69, the Vice President shall take an oath or affirmation administered by the President or a designated person, before assuming his/her office. In the oath, the Vice-President pledges to:
- Bear true faith and allegiance to the Constitution of India.
- Faithfully discharge the duties of the office.
As per the constitution of India, there are other conditions to the office of Vice President, which are as follows:
- The Vice-President should not be a member of either House of Parliament or any state legislature. If elected, they automatically vacate their seat in that House upon assuming office.
- The Vice-President should not hold any other office of profit.
Term of the Office of Vice President
The Vice-President holds office for five years, but can resign at any time by addressing a letter to the President.
However, the Vice-President can also be removed before completing the term through a resolution passed by a majority of Rajya Sabha members and agreed to by the Lok Sabha. The resolution can only be introduced in the Rajya Sabha and requires at least 14 days’ notice. No specific grounds for removal are mentioned in the Constitution.
The Vice-President can serve beyond the five-year term until a successor assumes office and is eligible for re-election for any number of terms.
As per Article 68 of the constitution, election to the office of Vice President shall be held in case of a vacancy in the Vice-President’s office due to:
- Expiry of term [Art 68 (1)]
- Resignation [Art 68 (2)]
- Removal [Art 68 (3)]
- Death [Art 68 (4)]
- Disqualification or invalid election [Art 68 (5)]
An election to fill the vacancy must occur before the term expires or as soon as possible in case of resignation, removal, death, or other reasons. The important point to note is that the newly elected Vice-President serves a full five-year term from the date of assuming office.
Functions of the Vice President
Now that we know how the VP is elected, let us look at the functions he/ she undertakes as per the constitution. The functions of the Vice-President of India are two-fold:
- Chairman of Rajya Sabha: The Vice-President acts as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, performing duties similar to the Speaker of the Lok Sabha. This role resembles that of the American Vice-President, who is also the Chairman of the Senate.
- Acting President: When the office of the President becomes vacant due to resignation, impeachment, death, or other reasons, the Vice-President assumes the role of Acting President.
- However, this is for a maximum period of six months, within which a new President must be elected.
- The Vice-President also takes over the President’s duties if the sitting President is unable to discharge his functions due to absence, illness, or other causes.
- During this time, the Vice-President does not perform his duties as Chairman of Rajya Sabha, which are instead handled by the Deputy Chairman.
Salary Of the Vice President of India
The Vice-President’s salary is determined by his role as Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, with no separate emoluments for acting as President. In 2018, his salary was increased to ₹4 lakh per month, and his pension was raised to 50% of his salary.
He also enjoys allowances, a furnished residence, medical, travel, and other facilities. However, when acting as President, he receives the salary and allowances of the President, not those of the Chairman of Rajya Sabha.
Discussion on the Indian Vice President and the US Vice President’s Office
The office of the Vice-President in India and the United States shares some similarities, but there are significant differences in their roles, powers, and responsibilities.
- Constitutional Role and Function
In India the Vice-President of India has two primary roles:
- Ex-officio Chairman of Rajya Sabha: The Vice-President presides over the Rajya Sabha (the Upper House of Parliament) and has powers similar to those of the Speaker of the Lok Sabha (the Lower House). In this capacity, the Vice-President’s role is primarily legislative and non-executive.
- Acting President: In case of a vacancy in the office of the President (due to death, resignation, or other reasons), the Vice-President acts as the President until a new President is elected.
- However, this role is temporary, limited to a maximum of six months. The Vice-President does not assume the full powers of the President, as the Indian system requires the election of a new President after the vacancy arises.
In the United States, the Vice President of the United States has a more direct executive role:
- President of the Senate: Like the Indian Vice-President, the U.S. Vice-President is the President of the Senate, but their role is more ceremonial, with the primary responsibility being to cast a tie-breaking vote in the Senate when necessary.
- Successor to the President: Unlike the Indian system, where the Vice-President temporarily acts as President, the U.S. Vice-President immediately succeeds to the presidency if the sitting President dies, resigns, or is removed from office.
- The Vice-President serves out the remainder of the President’s term, not just temporarily.
- This gives the U.S. Vice President more direct constitutional authority, as they can become the President with full powers, including the ability to make executive decisions, issue executive orders, and sign legislation into law.
2. Presidential Succession
- The Indian Vice-President does not succeed the President when the office becomes vacant for the remainder of the term. This is a temporary arrangement, typically lasting no more than six months. The Vice-President’s role as Acting President is limited in scope and duration.
- Whereas in the U.S. Vice President automatically succeeds to the presidency if the President dies, resigns, or is removed from office. The U.S. Constitution specifies that the Vice President assumes the full powers and duties of the President, including commanding the military, signing treaties, and issuing pardons. The Vice-President serves the remainder of the President’s term, which could be several years, depending on when the vacancy occurs.
3. Eligibility and Election
- The Vice-President of India is elected by an electoral college consisting of the members of both Houses of Parliament. The election is indirect, and the Vice-President is elected using a system of proportional representation by means of a single transferable vote. The Vice-President does not need to be a member of Parliament to run for office, but if elected, they must vacate their seat in Parliament. The Vice-President can serve a maximum of five years, with the possibility of re-election.
- The Vice-President of the U.S. is elected as part of a ticket with the President in a direct election by the people. Voters choose a President and Vice-President together, and they run on the same party ticket. The Vice-President serves a four-year term and is eligible for re-election for any number of terms, just like the President.
4. Executive Powers and Influence
- The Vice-President of India enjoys limited executive powers. When acting as President, the Vice-President temporarily takes on the President’s executive functions, but only in a caretaker capacity. The Vice-President does not have the power to make long-term decisions or policy changes in this role. The role is largely ceremonial with respect to the government’s daily functioning, and the Vice-President has little influence over national policy-making.
- The U.S. Vice President has a more influential role in the executive branch. As the President’s immediate successor, the Vice President is considered part of the President’s administration and may play a significant role in the decision-making process, often influencing key policies. The U.S. Vice President may also have substantial duties assigned by the President, including diplomatic or special assignments. If the Vice-President assumes the presidency, they gain full executive powers, including directing foreign and domestic policy.
Read More: Federalism explained
Copy the handwritten notes For Free