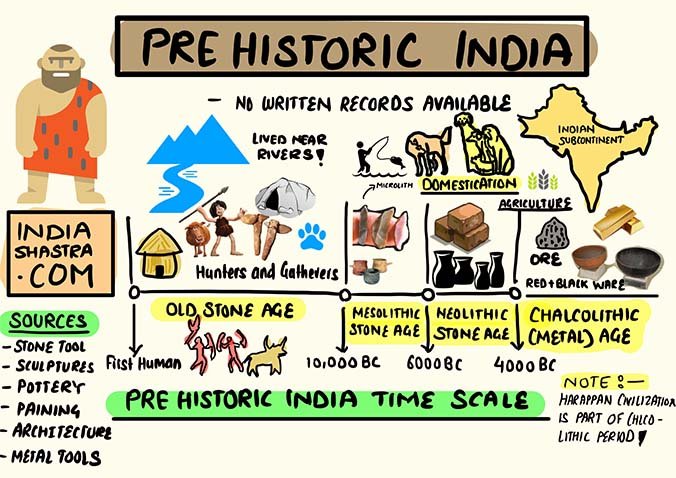
Prehistory is the period in human history before recorded events i.e no written records are available for prehistoric India. The research and development in archaeology help us to understand the life and culture of the people who lived in this period.
We can divide Prehistoric India into 4 ages,
-
The Palaeolithic (Old Stone Age),
-
Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age),
-
Neolithic (New Stone Age) and
-
The Metal Age.
However, these periods were not uniform throughout the Indian subcontinent.
How Historians Calculate dates?
-
Radiocarbon dating is used to calculate dates in history. It is based on measuring the loss of carbon in organic materials over a period of time.
-
Dendrochronology is another dating method. It refers to the number of tree rings in wood. The date of the wood is proportional to the number of tree rings.
Palaeolithic or Old Stone Age
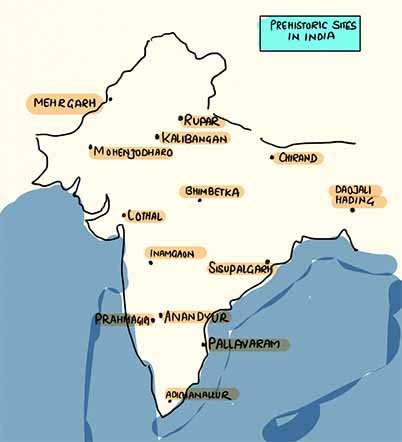
The Old Stone Age sites are scattered on the map of the Indian subcontinent. These sites are generally located near water sources. Most of them lived in huts made of leaves. Also, excavators found several rock shelters and caves used by Palaeolithic people.
Old Stone age people hunted animals and gathered edible plants and fruits. Hence, the name hunter-gatherers. They used stone tools, hand-sized and flaked-off large pebbles for hunting animals. People used quartzite, a hard rock for making stone tools.
The hunting of large animals would have required the combined effort of a group of people with large stone axes. We have little knowledge about their language and communication. The period before 10000 B.C. is assigned to the Old Stone Age.
Mesolithic or Middle Stone Age
The next stage of human life is called the Mesolithic or Middle Stone Age, which falls roughly from 10000 B.C. to 6000 B.C. It was the transitional phase between the Palaeolithic Age and the Neolithic Age.
Archaeologists found Mesolithic remains in,
-
Langhanjin, Gujarat
-
Adamgarhin, Madhya Pradesh
-
Rajasthan
-
Utter Pradesh
-
Bihar.
The paintings and engravings found at the rock shelters give an idea about the social life and economic activities of the Mesolithic people. Excavators found a different type of stone tools, not more than five centimetres in size,e called microliths.
The hunting-gathering pattern of life continued during this period. This age witnessed a shift from big animal hunting to small animal hunting. First of all, the use of bow and arrow also began during this period. Also, there began a tendency to settle for longer periods in an area. Therefore, the domestication of animals, horticulture and primitive cultivation started. Archaeologists found bones of a dog, a deer, a boar, and an ostrich on site. Furthermore, burials of the dead, along with some microliths and shell, weres found occasionally.
Neolithic Age
The chief characteristic features of the Neolithic culture are the practice of agriculture, domestication of animals, polishing of stone tools and the manufacture of pottery. In fact, the cultivation of plants and domestication of animals led to the emergence of village communities based on sedentary life.
-
Stone Tools: There was a great improvement in the technology of making tools. They used polished stone tools and axes for gathering and hunting.
-
Houses: Houses built of mudbricks instead of grass huts.
-
Pottery: Utensils made on wheels used for cooking and storing food grains.
-
Burials: Neolithic people buried dead in coffins (large urns)
-
Agriculture: Above all, there was an improvement in agriculture. Neolithic people cultivated wheat, barley, rice, millet.
-
Domestication: People domesticated sheep, goats, and cattle. Furthermore, they used cattle for cultivation and transport. Likewise, the people of Neolithic Age used clothes made of cotton and wool.
Metal Age
The Neolithic period is followed by the Chalcolithic (copper-stone) period when copper and bronze came to be used. The new technology of smelting metal ore and crafting metal artefacts is an important development in human civilisation. While they continued to use of stone tools. Some of the micro-lithic tools continued to be essential items. People began to travel for long distances to obtain metal ores. This led to a network of Chalcolithic cultures.
Iron Age followed the Chalcolithic period. Historians often correlate Iron Age with megaliths of South India. Megalith means Large Stone. These large stones covered burials. We can find such graves extensively in south India.
Some of the important megalithic sites are Hallurand Maskin Karnataka, Nagarjunakondain Pradesh, and Adichchanallur Tamil Nadu. Excavators found black and red pottery, iron artefacts such as hoes and sickles and small weapons in the burial pits.
Read more: Modern India
Locations of Prehistoric Sites in India